Generative AI technology is gaining popularity, but do businesses have guidelines or policies in place to regulate its use? GetApp surveyed 660 employees who use generative AI tools about guidance on the usage of such tools and how to make the best of this technology.
What we will cover
While the capabilities of generative AI technology present significant opportunities, they may also raise some concerns. According to a study by Gartner, 70% of organizations will identify the ethical and sustainable use of AI among their top concerns by 2025.
Establishing a responsible approach to generative AI technology implementation can allow organizations to build trust with employees, stakeholders, and customers. While Canada does not have any AI-specific law at the moment, Canadian legislators are addressing the use of AI in the context of automated decision-making. Quebec’s private sector law (Quebec Privacy Law), as amended by Bill 64 is the first type of legislation in Canada that explicitly regulates ‘automated decision-making’.
To understand if Canadian firms have any policies or regulations in place for using generative AI technology, GetApp surveyed 660 full-time or part-time employees who’ve been using generative AI tools at work at least a few times per month. The full methodology is at the bottom of this article.
Over-reliance on AI and privacy among top ethical concerns for generative AI usage
According to Avivah Litan, a Gartner VP Analyst, some of the biggest concerns around generative AI include trust, security, deepfakes, data privacy, hallucinations, cybersecurity risks, and copyright issues. Since generative AI models are usually trained on huge datasets from multiple sources, including the internet, and so in some cases, the data source could be unknown, which could be harmful to businesses.
Similarly, we asked our survey-takers what ethical concerns they have when it comes to generative AI systems.

Delving deeper into the issue, we asked our respondents about the risks that their companies may get exposed to while using generative AI tools. Cybersecurity risks came out on top of the list of risks for 46% of the respondents, followed by regulatory compliance/legal risks (34%), personal/individual privacy risks (33%), lack of explainability (31%), and copyright issues (31%).
Considering the ethical concerns that companies may have surrounding the use of generative AI, organizations should implement meticulous reviews of the output produced by generative AI models to spot biased results or misinformation.
Tips for SMEs:
To use generative AI tools in a safer way, companies may use:
- Cybersecurity software to protect systems and confidential data
- Policy management software to revise, re-create, or review the updated policies to ensure transparency
- Compliance software to ensure regulatory compliance across all their work operations
- Security awareness training software to create training and awareness programs around the usage of generative AI tools for employees
How do respondents monitor the quality of output produced by generative AI tools?
Generative AI tools can potentially produce unexpected outputs since they are trained on large datasets from multiple sources, which may or may not be verified or reliable. Taking this into account, it is ideally crucial to assess all the output generated for accuracy.
We asked user respondents who admitted to using AI openly at their workplace how they check for the accuracy of generative AI results. Our sample identified several options:
- 40% of the users say that their company collects employee feedback via surveys
- 34% of generative AI users have some key performance indicators (KPIs) in place to monitor generative AI outputs
- 33% of the surveyed users say that a dedicated team evaluates such results
- 31% of surveyed users say that they compare human outputs with AI outputs
- 12% of the respondents say that their company does not monitor these results as of now but they feel they should start doing it
- Only 5% of respondents say that they don’t monitor such results and they don’t find it necessary to do so
Considering that only 5% of users don’t monitor results generated by AI tools, we can infer that most respondents feel that there is a need to evaluate and verify such content. As such, it can be important to have some techniques and methods in place for companies to perform these checks on a regular basis.
Have companies put any regulations in place to use generative AI tools at work?
Security is a vital factor to consider when implementing any new technology in business operations. The use of generative AI can involve inputting sensitive information —such as customer records, commercial content, or financial data— which can be crucial to a company’s operations. In fact, our study reveals that 81% of the surveyed Canadian employees inform their company that they use generative AI at work, while 19% of them have not informed their employers.
Workers should ideally get consent from their managers or employers while using generative AI tools so that they can make the right use of the technology. Organizations should also clearly communicate the practical usage guidelines of generative AI tools for employees so they always use these tools when required.
Considering this, we asked the subset of respondents who openly use AI tools —whom we will refer to as users— if their company has implemented any guidelines at their workplace.
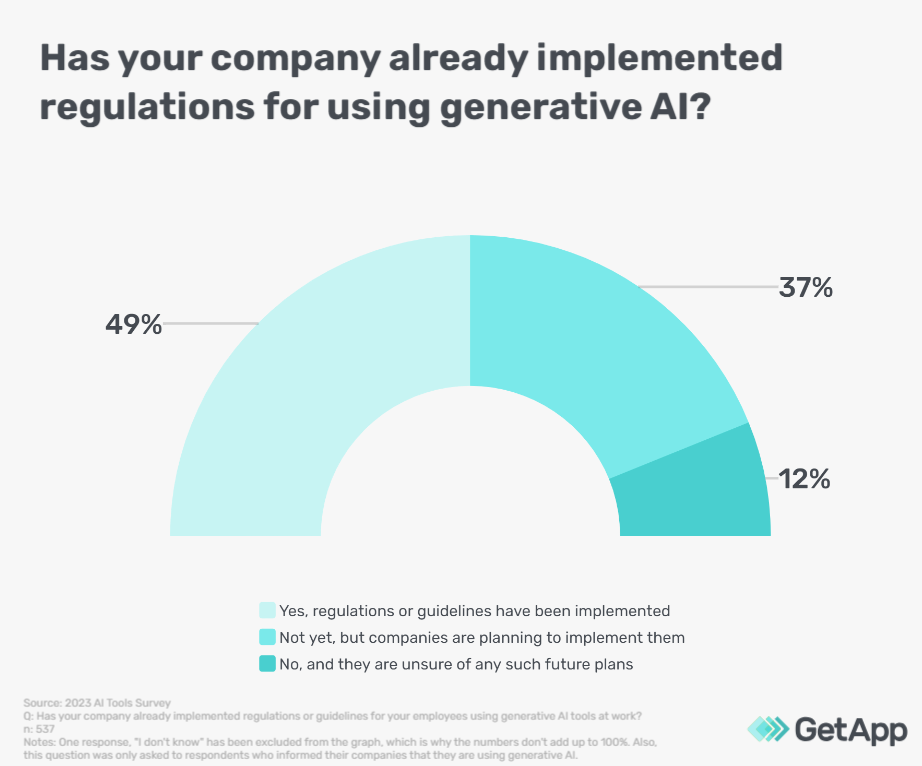
Bearing in mind that nearly half of the users (49%) say their company has some regulations in place for the best use of generative AI at work, we further asked this group about the kind of guidelines they have implemented in their organizations. Here are the results:
- 60% of the respondents say that guidelines have been established for the proper usage of approved generative AI tools
- 57% of them say that company policies have been established to ensure that generative AI tools are used in compliance with regulations and laws
- 47% of the survey takers say that in their company, employees have to undergo training on the right use of generative AI tools, as well as data privacy and ethical considerations
- 38% of the respondents state that approval from managers is required before they can use generative AI platforms for specific tasks
- 23% of them reported that a curated list of approved generative AI tools has been created
- 15% of the respondents said that employees need to review and sign the company policy before using generative AI tools
Some factors to consider when establishing a generative AI usage policy for your business:
- Ensure privacy: Generative AI tools usually gather information in order to produce output. As such employers, should make it clear to employees that no sensitive or confidential commercial information should be shared as a prompt while using generative AI tools.
- Avoid bias: Generative AI tools may represent the bias of data inputs. For example, if the data used to train a generative AI tool is biased towards any specific gender or race, the system could produce biased outputs. Although it may not be possible to completely eliminate AI-related biases, business users should potentially review generated outputs to avoid or correct biased results.
- Aim for transparency: Companies should clearly mention in their policy document how employees can use AI tools in their daily work operations. Organizations should also tell their clients or business partners whether and how these tools are being used in collaboration with their services/products.
The impact of generative AI on jobs
Some generative AI tools —such as Midjourney and ChatGPT— can now write articles, and programming codes and create commercial designs in just a few seconds. This is why employees may have concerns over AI replacing their jobs in the coming years. We asked our respondents how they felt about this and here’s what they had to say:
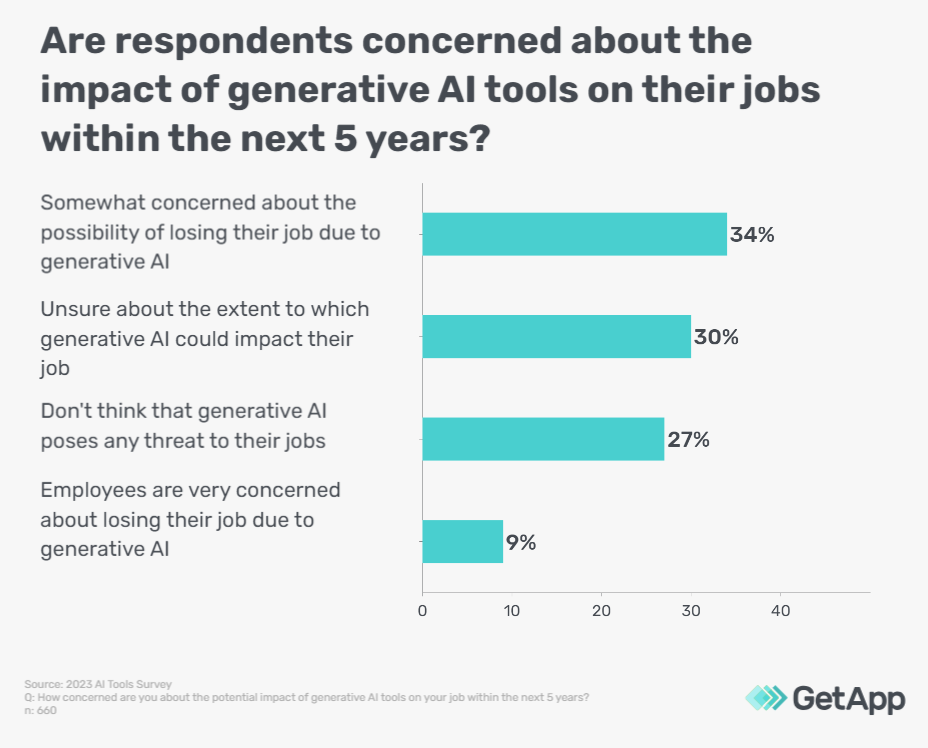
Clearly, 34% of respondents are somewhat concerned, while 30% are unsure about the impact of this tech on their job. On the other hand, 27% feel that generative AI doesn’t pose any threat to their jobs. There is a fair amount of uncertainty when it comes to this tech’s impact on jobs. This could be because the latest generative AI tools such as ChatGPT are fairly new and the true effects cannot be gauged right now.
However, according to research by Gartner, the impact on global jobs will be neutral; there will not be a net decrease or increase through 2026. The same report also went on to state that AI-based solutions will lead to more than half a billion net new jobs in the next 10 years.
4 ways to minimize the risks of using generative AI tools for businesses
According to Mondaq, investments in generative AI are expected to hit US$42.6 billion by the end of 2023. This projection could be based on the potential of generative AI tools to boost productivity and drive innovation, as stated in part 1 of this survey report.
In addition, a combined total of 92% of surveyed generative AI users reported giving either some level or high level of importance to the implementation of this technology, further underlining the interest in this tech.
However, it may be important to keep in mind that every new technology might bring some potential risks along with benefits. But that does not mean that organizations should stop exploring such new tools and technologies to leverage their benefits. Rather, businesses should follow appropriate steps to minimize the risks of generative AI and use it to their advantage. Here are a few suggestions:
- Test tools internally:
Before a business thinks about implementing generative AI platforms in their day-to-day work operations, they may consider testing it extensively with their employees and internal stakeholders to understand how these tools can be used optimally. - Identify the right tools:
Since you may find a variety of free tools available in the market, you should carefully look for the tools that have been thoroughly vetted and offer some kind of reliability to businesses. - Analyze the level of supervision required:
Consider what level of access control should be given to employees and carefully decide whether the use of specific generative AI tools should be supervised by any senior leadership authorities, and if so, by whom. - Create a well-crafted policy for the usage of generative AI tools:
Businesses should have a detailed policy that lays out the framework for such use as well as the consequences an employee or a stakeholder may have to face for misusing any sensitive data.
Methodology
The data for GetApp’s Generative AI Tools Survey was collected in June 2023 and comprises answers from 660 respondents. We selected our survey sample based on the following selection criteria:
- Canadian resident
- Between 18 and 65 years of age
- Either full-time or part-time employed in a company and use laptops/computers to perform daily tasks at work
- Must understand the definition of generative AI: “Generative AI (GAI) refers to a type of artificial intelligence that is capable of generating new, original content such as images, videos, music, code, or text. It typically uses deep learning techniques and neural networks to analyze and learn from large datasets and uses this information to generate content that resembles human creations. Some examples of generative AI tools are ChatGPT, Bard, and DALL-E.”
- Must use generative AI tools at least a few times per month
